Inference at the Edge
How to Work Securely and Offline with Language Models
Dylan Goldblatt, Ph.D.
Kennesaw State University
Slides:
inference-slides.vercel.app
Extras:
inference-extras.vercel.app

Today's Journey
- Why local inference matters
- How to select the right foundation model
- Run local LLMs with RAG functions
- Transcribe audio and video files locally
- Securing remote inference
1. Why Local Inference Matters
Key Benefits
- Privacy & data security
- Independence from connectivity
- Low latency, high speed
- Control over updates and usage
- Personalization without sharing data
Privacy & Security
- Your input data never leaves your device
- No one else can access, store, or analyze it
- No server logs of your queries exist
- No training on your proprietary information
Availability & Cost
- Works without internet access
- Works in secure environments
- Works without downtimes and outages
- Works without a dedicated budget/subscription
Speed & Control
- Fast responses
- Full control over model versions
- No surprise interface or functionality changes
- You decide when to update—or not
2. Selecting Foundation Models
Choosing the Right Model
- Find a model that suits your hardware
- Match a model to your needs
- Use quantization to adjust for both

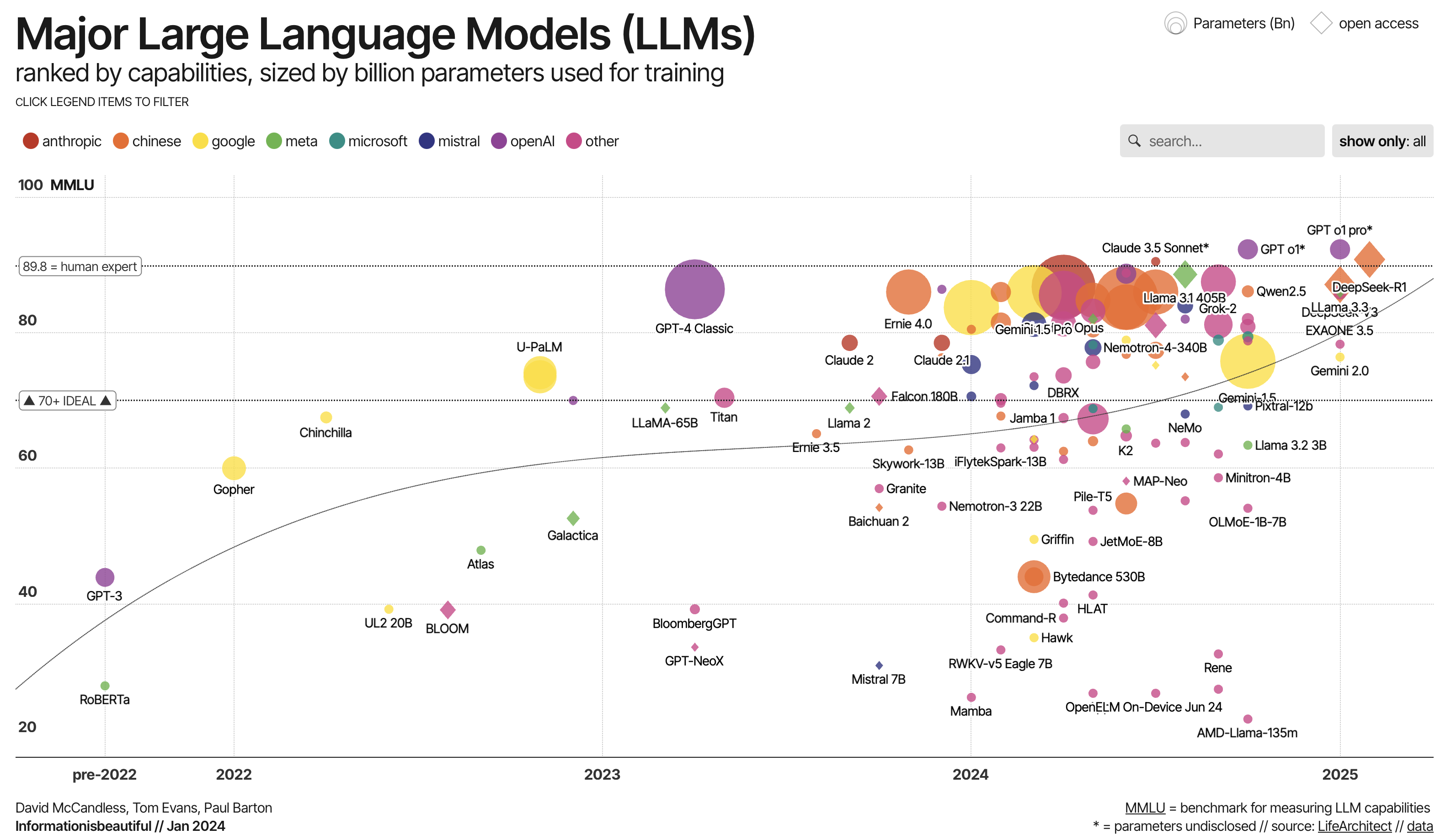
LLaMA (Meta)
- Generous context windows
- Excellent size-quality balance
Mistral
- Perfect for limited hardware
- Good balance of capabilities
Gemma (Google)
- Perfect for limited hardware
- Good balance of capabilities
Phi (Microsoft)
- High speed and small size
- Can run on edge hardware including phones
Qwen (Alibaba)
- Competes with larger, private models
- Less computationally demanding vs. DeepSeek
DeepSeek
- Matches private models in quality
- Disallowed for USG work computers
| LLM Family | Model Sizes | Multilingual | Coding Strength | Context | MMLU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Google Gemma (3) | 27B (12B, 4B, 1B) | Yes (140+ langs) | Moderate (basic coding ability) | 128k tokens | ~67.5% |
| Microsoft Phi (Phi-4) | 5.6B, 3.8B (plus 14B) | Yes (broadly multilingual) | Yes – excels for its size | up to 128k tokens | ~69–78% |
| Mistral (Large 2) | 123B (also 24B, 7B) | Yes (dozens of langs) | Yes – strong; trained heavily on code | 128k tokens | ~84.0% |
| Alibaba Qwen (2.5) | 72B (32B, 14B, 7B) | Yes (29+ languages) | Yes – esp. 7B Coder variant | 128k tokens | ~86% |
| Meta LLaMA (3.1) | 405B, 70B, 8B | Partial (8 languages) | Yes – state-of-the-art (matches GPT-4-level) | 128k tokens | ~87.3% |
| DeepSeek (R1) | 671B (MoE) | Yes (EN/ZH high proficiency) | Yes – top-tier reasoning & code | 128k tokens | ~90.8% |
Matching LLMs to GPUs
- Macs are the best "default" work option.
- Most work PCs lack dedicated VRAM
- Most work PCs can run small models
- Parameter size (B) is roughly the VRAM target
- Estimate LLM capabilities before purchasing
- Nvidia-based computers are the best choice.
Quantization
Quantization compresses LLMs by storing weights in fewer bits:
- Full precision (FP16): ~14GB for a 7B model
Highest quality, highest memory - 8-bit (INT8): ~7GB
Excellent quality, half the memory - 4-bit (INT4): ~3.5GB
Slight quality tradeoff, significant memory savings

Common Quantization Formats
- GGUF (GGML Unified Format)
Optimized for CPUs and Apple Silicon; portable and widely supported - GPTQ
Popular for GPU acceleration; fast inference - AWQ (Activation-aware Quantization)
Advanced technique balancing accuracy and speed - MLX (Metal acceleration)
Optimized specifically for Apple hardware; offers ~20-30% performance improvement
3. Run local LLMs with RAG functions
User-Friendly Local Apps
- LM Studio: Closed-source, first-class citizen
- Jan.ai: Open-source, "calmer" user experience
- Ollama: High efficiency but lacks a UI
- AnythingLLM: Multifunctionality, RAG focus
LM Studio
- Cross-platform: macOS, Windows, Linux
- Built-in model library with easy downloads
- Completely offline operation after setup
- ChatGPT-like interface running locally
- Basic RAG capabilities included
- Powered by llama.cpp under the hood
Live Demo
LM Studio (MAC)
Jan.ai
- Fully open-source alternative (AGPL licensed)
- Similar experience to LM Studio
- Multiple backends (llama.cpp, TensorRT)
- Evolving rapidly with new features
- Community-driven development
- Local API server capabilities
Demo
Jan (PC)
Mac Specific "Unlock"
Apple Silicon Macs have a software limit on GPU memory:
- Default: ~75% of physical RAM available for GPU
- Advanced users can modify this limit by:
- Disabling System Integrity Protection (SIP)
- Modifying system graphics driver settings
- Only recommended for dedicated AI machines
Most users with 7B-13B models won't need this
sudo sysctl iogpu.wired_limit_mb=<mb>
Notes on RAG
- Feed your notes, PDFs, research papers
- Query in natural language
- Get responses based on your personal data
- All while keeping information private
NVIDIA ChatRTX (PC)
- Specialized for NVIDIA RTX 30/40/50 series GPUs
- Blazingly fast RAG optimized for tensor cores
- Document and image search
- Voice input
- Remarkably smooth performance
- Windows 11 with modern NVIDIA GPU required
Demo
ChatRTX (PC)
RAG to Riches (R2R)
- Production-grade RAG framework
- Knowledge graphs
- Multi-step reasoning
- Hybrid search (keywords + vectors)
- Tool-using agents
- More complex setup but extremely powerful
4. Transcribe audio and video files locally
Local Audio Transformation
- State-of-the-art speech recognition
- Open-source and runs locally
- Multiple sizes (tiny → large)
- Supports 99 languages
- Transcribe without sharing audio
MacWhisper
- Native macOS app for Whisper
- Metal acceleration for Apple Silicon
- Excellent transcription capabilities
- Speaker diarization (who spoke when)
- Punctuation and formatting
Free and paid Pro versions
https://goodsnooze.gumroad.com/l/macwhisper
Live Demo
MacWhisper (MAC)
5. Securing remote inference
Remote LLMs via API
- Best quality & performance
- Very large context windows (100K+)
- No local device hardware constraints
- Incorporate inference into software
- Economical Pay-for-Usage model
- OpenRouter vs. LLM Companies
- Improved security
Securing Remote LLMS
- Strip sensitive information (e.g., names)
- Use providers with strong data guarantees
- Segment your usage between local for sensitive tasks and remote for public-domain questions
- Hugging Face Private Inference
- Your own server running open models
- Remote but still under your control
Conclusion
By managing your inference at the edge, you:
- Reclaim control over privacy and security
- Use cloud services selectively
- Work effectively even when disconnected
- Control your AI experience completely
Book an AI Consultation

KSU AI Community

Discussion
Thank you for attending the AI Fair!
